Trending Laptops
Trending Laptops
About Laptops
Laptops are portable computers designed for versatility, making them suitable for a wide range of tasks, from office work and education to gaming and creative pursuits. They come in various shapes, sizes, and specifications to cater to different needs. Here’s an overview of key aspects to consider when exploring laptops:
Types of Laptops
• Ultrabooks / Lightweight Laptops

- Thin, lightweight, and highly portable, designed for everyday tasks and productivity.
- Examples: MacBook Air, Dell XPS 13, ASUS ZenBook
- Pros:
- Extremely portable and thin, perfect for travel.
- Generally offer long battery life and fast performance for light tasks.
- Cons:
- Limited upgrade options.
- Typically lack high-performance GPUs, so they’re not suitable for gaming or intensive tasks.
Gaming Laptop
- High-performance laptops with dedicated GPUs for gaming and demanding tasks
- Examples: Razer Blade, ASUS ROG Zephyrus, Alienware m15
- Pros:
- High-performance CPUs and dedicated GPUs for gaming and creative work.
- Often come with high-refresh-rate screens and RGB lighting.
- Cons:
- Heavy, with shorter battery life due to high power usage.
- Can overheat, requiring more frequent maintenance (e.g., fan cleaning).

• 2-in-1 Laptops
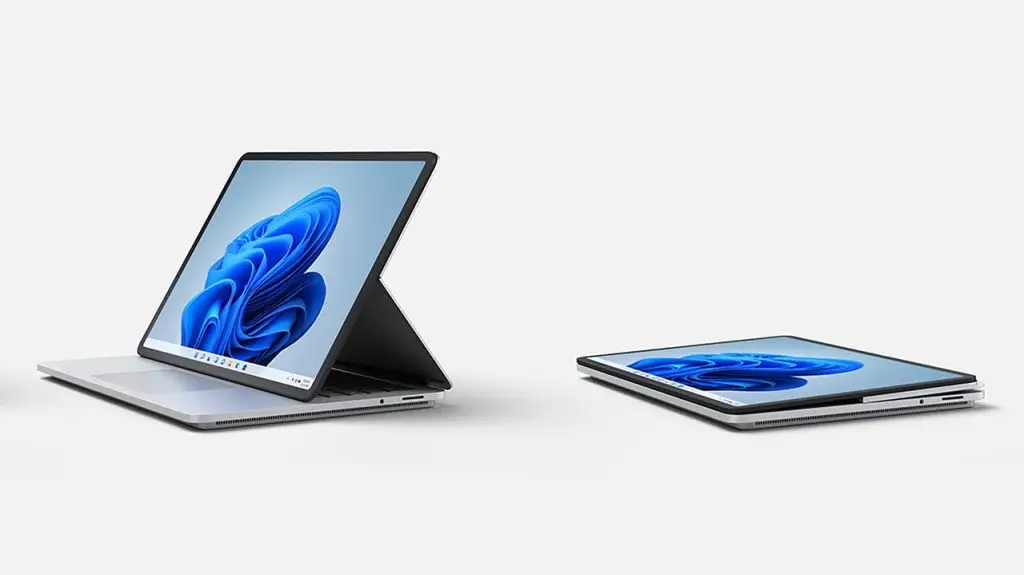

- Convertible devices that can function as both a laptop and a tablet
- Examples: Microsoft Surface Pro, HP Spectre x360, Lenovo Yoga
- Pros:
- Versatile, can be used as a laptop or a tablet.
- Touchscreen and stylus support, great for artists and note-taking.
- Cons:
- Durability can be a concern with the hinge mechanism.
- Performance can be lower compared to traditional laptops in the same price range.
• Business Laptops
- Durable and secure laptops tailored for work environments
- Examples: Lenovo ThinkPad series, Dell Latitude, HP EliteBook
- Pros:
- Durable, often MIL-STD tested, and built for long-lasting performance.
- Feature-rich for productivity, with good keyboards, ports, and security features.
- Cons:
- Generally more expensive, especially with business-focused features.

• Workstation Laptops
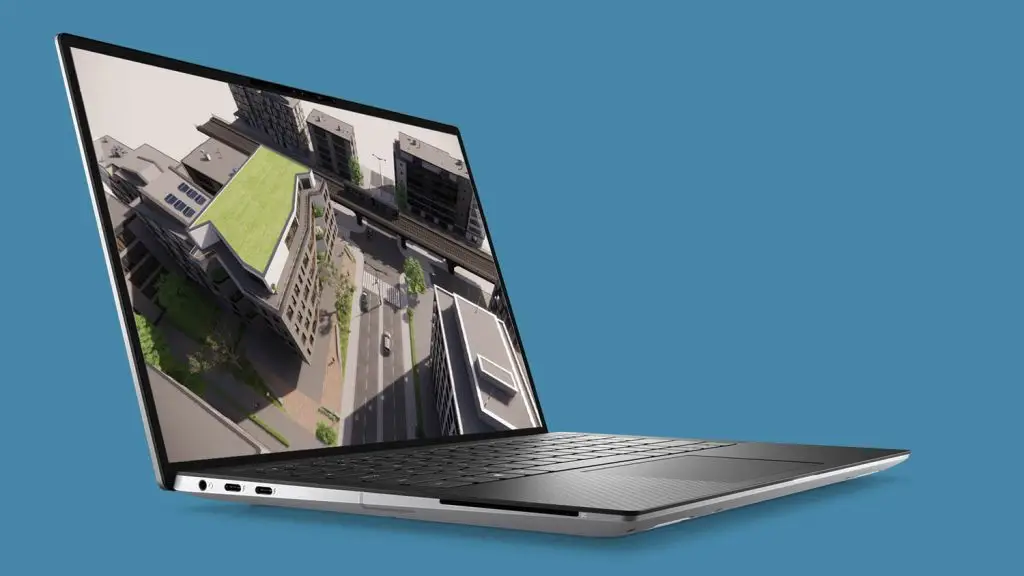

- essential for specialized, high-demand tasks
- Examples: Dell Precision, HP ZBook, Lenovo ThinkPad P Series
- Pros:
- Powerful processors and GPUs tailored for professional tasks (e.g., CAD, 3D rendering).
- Often have ISV (Independent Software Vendor) certifications for software like AutoCAD and SolidWorks.
- Cons:
- Expensive and bulky, typically not designed for portability.
• Budget Laptops / Chromebooks
- Lightweight laptops running Chrome OS, great for web-based tasks and students.
- Examples: Acer Chromebook, HP Stream, Lenovo IdeaPad
- Pros:
- Affordable, great for basic tasks like web browsing, word processing, and streaming.
- Chromebooks, in particular, are lightweight and have good battery life.
- Cons:
- Limited performance, especially for multitasking or heavy apps.
- Minimal storage and lower-quality displays on budget models.

Specifications to Consider
- Processor (CPU): Determines performance. Common options include Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9, AMD Ryzen, and Apple M1/M2 chips.
- RAM: Affects multitasking. 8GB is sufficient for most users; 16GB or more is ideal for power users.
- Storage: SSDs (Solid State Drives) are faster and more reliable than HDDs. Look for at least 256GB; more is better for heavy users.
- Graphics (GPU): Important for gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering. Options include integrated GPUs (e.g., Intel Iris Xe) or dedicated GPUs (e.g., NVIDIA GeForce, AMD Radeon).
- Display: Consider resolution (Full HD, 4K), size (13″, 15″, 17″), and type (OLED, IPS, TN).
- Battery Life: Portability often depends on good battery life. Aim for 8+ hours for work on the go.
Operating Systems
- Windows: Versatile and widely used, suitable for gaming, business, and general use.
- macOS: Found on Apple laptops, known for sleek design and creative software support.
- Chrome OS: Lightweight, secure, and web-focused.
- Linux: Preferred by developers and tech enthusiasts for customization.
Popular Brands
Dell, HP, Lenovo, ASUS, Acer, Apple, Microsoft, and Razer are leading brands offering diverse options
Additional Features
- Ports: USB-C, Thunderbolt, HDMI, and headphone jacks for connectivity.
- Keyboard: Backlit keyboards for low-light typing.
- Build Quality: Aluminum vs. plastic, durability, and design.
- Cooling: Essential for gaming or performance laptops.
General Pros of Laptops
- Portability – Laptops are compact and easy to carry, allowing you to work or play from almost anywhere with battery power.
- Space Efficiency – With everything integrated (keyboard, trackpad, screen), laptops take up less space than desktops, making them ideal for smaller work areas.
- All-in-One Functionalit – Most laptops come with built-in webcams, microphones, and speakers, making them convenient for communication, multimedia, and work.
- Battery Backup – Laptops allow you to keep working even during power outages, as they can run for hours on battery.
- Energy Efficiency – Laptops generally consume less power than desktops, which can lead to energy savings over tim
General Cons of Laptops
- Limited Upgradability – Laptops are compact and easy to carry, allowing you to work or play from almost anywhere with battery power.
- Lower Performance for Price – For the same price, a desktop generally offers better performance than a laptop, especially in graphics and processing power.
- Thermal Constraints – Due to their compact size, laptops are prone to overheating, particularly under heavy usage (like gaming), which can limit performance.
- Shorter Lifespan – Laptops often wear out faster than desktops, especially with battery degradation over time. They’re also more susceptible to damage from drops or spills.
- More Expensive Repairs – Laptop repairs can be pricier due to compact, specialized parts, and in some cases, a broken component (like a screen) may require replacing the entire unit.
Conclusion
When choosing a laptop, the ideal choice depends on your specific needs, preferences, and budget. Here are some concluding tips to help you make an informed decision:
Purpose Matters: Consider what you’ll primarily use the laptop for:
- Everyday use: Look for a budget-friendly option with decent processing power and battery life.
- Gaming: Opt for a gaming laptop with a powerful GPU, high refresh rate, and good cooling.
- Professional work: Prioritize performance, portability, and software compatibility (e.g., MacBook for creatives or business-class laptops for professionals).
- Students: Look for lightweight, long battery life, and affordability.